链表必刷题第二部分
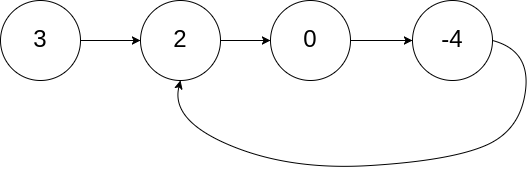
141.环形链表
给你一个链表的头节点 head ,判断链表中是否有环。
如果链表中存在环 ,则返回 true 。 否则,返回 false 。
解题思路
采用快慢指针法。步骤如下:
- 初始化两个指针
slow和fast,都指向链表头节点head。 - 同时移动这两个指针,
slow指针每次移动一步,fast指针每次移动两步。 - 如果链表中存在环,那么快慢指针最终会相遇。如果快指针遇到
null,说明链表没有环。 - 如果快慢指针相遇,返回
true,表示链表中存在环;否则,返回false。
/**
* Definition for singly-linked list.
* struct ListNode {
* int val;
* ListNode *next;
* ListNode(int x) : val(x), next(NULL) {}
* };
*/
class Solution {
public:
bool hasCycle(ListNode *head) {
if(head == nullptr) {
return false;
}
ListNode* fast = head -> next, *slow = head;
while(fast != slow) {
if(fast == nullptr || fast->next == nullptr) {
return false;
}
fast = fast->next->next;
slow = slow->next;
}
return true;
}
};
/**
* Definition for singly-linked list.
* class ListNode {
* int val;
* ListNode next;
* ListNode(int x) {
* val = x;
* next = null;
* }
* }
*/
public class Solution {
public boolean hasCycle(ListNode head) {
if (head == null) {
return false;
}
ListNode fast = head.next, slow = head;
while (fast != slow) {
if (fast == null || fast.next == null) {
return false;
}
fast = fast.next.next;
slow = slow.next;
}
return true;
}
}
func hasCycle(head *ListNode) bool {
if head == nil {
return false
}
fast, slow := head.Next, head
for fast != slow {
if fast == nil || fast.Next == nil {
return false
}
fast = fast.Next.Next
slow = slow.Next
}
return true
}
19.删除链表的倒数第 N 个结点
给你一个链表,删除链表的倒数第
n个结点,并且返回链表的头结点。
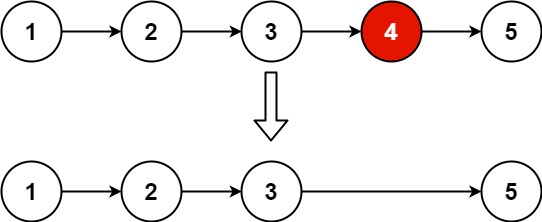
解题思路
可以使用一次遍历的双指针法。步骤如下:
- 创建一个虚拟头节点
dummy,并创建一个指针cur指向虚拟头节点。这样可以处理需要删除的节点为链表头节点的特殊情况。 - 初始化两个指针
first和second,都指向虚拟头节点。 - 将
first指针向前移动n个节点。如果链表的长度小于n,则直接返回链表的头节点,因为不需要删除任何节点。 - 同时移动
first和second指针,直到first指针到达链表的尾部。在移动过程中,保持两个指针之间的距离为n个节点。 - 当
first指针到达尾部时,second指针指向倒数第n+1个节点。更新second指针的next指针,使其指向倒数第n-1个节点,从而删除倒数第n个节点。 - 返回虚拟头节点的下一个节点,即为删除倒数第
n个节点后的链表头节点。
class Solution {
public:
ListNode* removeNthFromEnd(ListNode* head, int n) {
ListNode* dummy = new ListNode(-1);
dummy->next = head;
ListNode* first = dummy;
ListNode* second = dummy;
for (int i = 0; i <= n; ++i) {
first = first->next;
}
while (first != nullptr) {
first = first->next;
second = second->next;
}
second->next = second->next->next;
return dummy->next;
}
};
/**
* Definition for singly-linked list.
* public class ListNode {
* int val;
* ListNode next;
* ListNode() {}
* ListNode(int val) { this.val = val; }
* ListNode(int val, ListNode next) { this.val = val; this.next = next; }
* }
*/
public class Solution {
public ListNode removeNthFromEnd(ListNode head, int n) {
ListNode dummy = new ListNode(-1);
dummy.next = head;
ListNode first = dummy;
ListNode second = dummy;
for (int i = 0; i <= n; ++i) {
first = first.next;
}
while (first != null) {
first = first.next;
second = second.next;
}
second.next = second.next.next;
return dummy.next;
}
}
/**
* Definition for singly-linked list.
* type ListNode struct {
* Val int
* Next *ListNode
* }
*/
func removeNthFromEnd(head *ListNode, n int) *ListNode {
dummy := &ListNode{Val: -1}
dummy.Next = head
first := dummy
second := dummy
for i := 0; i <= n; i++ {
first = first.Next
}
for first != nil {
first = first.Next
second = second.Next
}
second.Next = second.Next.Next
return dummy.Next
}
23.合并K个升序链表
给你一个链表数组,每个链表都已经按升序排列。请你将所有链表合并到一个升序链表中,返回合并后的链表。
解题思路一:归并
可以采用归并排序。步骤如下:
- 将问题拆分为子问题:将链表数组拆分为两半,左边链表数组和右边链表数组。
- 递归解决子问题:对左右两边的链表数组分别递归地进行合并操作。递归的基本情况是链表数组长度为 1,此时直接返回链表数组中的唯一链表。
- 合并子问题的解:将递归处理后的左右两边链表进行合并。我们可以使用一个辅助函数
merge_two_lists,该函数可以合并两个有序链表为一个有序链表。
解题思路二:优先队列
优先队列的思路如下:
创建一个小顶堆(优先队列),用于存储各个链表的当前节点。
遍历链表数组,将每个链表的头节点加入优先队列。
创建一个虚拟头节点
dummy和一个指针cur,用于构建合并后的链表。当优先队列非空时,执行以下操作:
弹出优先队列中最小的节点,即当前所有链表中最小的节点。
将弹出的节点加入合并后的链表,并更新指针
cur。如果弹出的节点所在链表还有剩余节点,将下一个节点加入优先队列。
当优先队列为空时,合并操作完成。返回虚拟头节点的下一个节点,即为合并后的链表头节点。
// 归并
class Solution {
public:
ListNode* mergeKLists(vector<ListNode*>& lists) {
if (lists.empty()) return nullptr;
return mergeKListsHelper(lists, 0, lists.size() - 1);
}
ListNode* mergeKListsHelper(vector<ListNode*>& lists, int left, int right) {
if (left == right) {
return lists[left];
}
int mid = left + (right - left) / 2;
ListNode* leftList = mergeKListsHelper(lists, left, mid);
ListNode* rightList = mergeKListsHelper(lists, mid + 1, right);
return mergeTwoLists(leftList, rightList);
}
ListNode* mergeTwoLists(ListNode* l1, ListNode* l2) {
ListNode dummy(-1);
ListNode* tail = &dummy;
while (l1 && l2) {
if (l1->val < l2->val) {
tail->next = l1;
l1 = l1->next;
} else {
tail->next = l2;
l2 = l2->next;
}
tail = tail->next;
}
tail->next = l1 ? l1 : l2;
return dummy.next;
}
};
// 优先队列
#include <queue>
class Solution {
public:
struct ListNodeCompare {
bool operator()(const ListNode* a, const ListNode* b) const {
return a->val > b->val;
}
};
ListNode* mergeKLists(vector<ListNode*>& lists) {
if (lists.empty()) return nullptr;
priority_queue<ListNode*, vector<ListNode*>, ListNodeCompare> queue;
for (ListNode* node : lists) {
if (node != nullptr) {
queue.push(node);
}
}
ListNode dummy(-1);
ListNode* cur = &dummy;
while (!queue.empty()) {
ListNode* minNode = queue.top();
queue.pop();
cur->next = minNode;
cur = cur->next;
if (minNode->next != nullptr) {
queue.push(minNode->next);
}
}
return dummy.next;
}
};
/**
* Definition for singly-linked list.
* public class ListNode {
* int val;
* ListNode next;
* ListNode() {}
* ListNode(int val) { this.val = val; }
* ListNode(int val, ListNode next) { this.val = val; this.next = next; }
* }
*/
// 归并
public class Solution {
public ListNode mergeKLists(ListNode[] lists) {
if (lists == null || lists.length == 0) return null;
return mergeKListsHelper(lists, 0, lists.length - 1);
}
private ListNode mergeKListsHelper(ListNode[] lists, int left, int right) {
if (left == right) {
return lists[left];
}
int mid = left + (right - left) / 2;
ListNode leftList = mergeKListsHelper(lists, left, mid);
ListNode rightList = mergeKListsHelper(lists, mid + 1, right);
return mergeTwoLists(leftList, rightList);
}
private ListNode mergeTwoLists(ListNode l1, ListNode l2) {
ListNode dummy = new ListNode(-1);
ListNode tail = dummy;
while (l1 != null && l2 != null) {
if (l1.val < l2.val) {
tail.next = l1;
l1 = l1.next;
} else {
tail.next = l2;
l2 = l2.next;
}
tail = tail.next;
}
tail.next = (l1 != null) ? l1 : l2;
return dummy.next;
}
}
// 优先队列
public class Solution {
public ListNode mergeKLists(ListNode[] lists) {
if (lists == null || lists.length == 0) return null;
PriorityQueue<ListNode> queue = new PriorityQueue<>((a, b) -> a.val - b.val);
for (ListNode node : lists) {
if (node != null) {
queue.offer(node);
}
}
ListNode dummy = new ListNode(-1);
ListNode cur = dummy;
while (!queue.isEmpty()) {
ListNode minNode = queue.poll();
cur.next = minNode;
cur = cur.next;
if (minNode.next != null) {
queue.offer(minNode.next);
}
}
return dummy.next;
}
}
// 归并
func mergeKLists(lists []*ListNode) *ListNode {
if len(lists) == 0 {
return nil
}
return mergeKListsHelper(lists, 0, len(lists)-1)
}
func mergeKListsHelper(lists []*ListNode, left, right int) *ListNode {
if left == right {
return lists[left]
}
mid := left + (right-left)/2
leftList := mergeKListsHelper(lists, left, mid)
rightList := mergeKListsHelper(lists, mid+1, right)
return mergeTwoLists(leftList, rightList)
}
func mergeTwoLists(l1, l2 *ListNode) *ListNode {
dummy := &ListNode{Val: -1}
tail := dummy
for l1 != nil && l2 != nil {
if l1.Val < l2.Val {
tail.Next = l1
l1 = l1.Next
} else {
tail.Next = l2
l2 = l2.Next
}
tail = tail.Next
}
if l1 != nil {
tail.Next = l1
} else {
tail.Next = l2
}
return dummy.Next
}
// 优先队列
import (
"container/heap"
)
type ListNodeHeap []*ListNode
func (h ListNodeHeap) Len() int { return len(h) }
func (h ListNodeHeap) Less(i, j int) bool { return h[i].Val < h[j].Val }
func (h ListNodeHeap) Swap(i, j int) { h[i], h[j] = h[j], h[i] }
func (h *ListNodeHeap) Push(x interface{}) {
*h = append(*h, x.(*ListNode))
}
func (h *ListNodeHeap) Pop() interface{} {
old := *h
n := len(old)
x := old[n-1]
*h = old[0 : n-1]
return x
}
func mergeKLists(lists []*ListNode) *ListNode {
if len(lists) == 0 {
return nil
}
h := &ListNodeHeap{}
heap.Init(h)
for _, node := range lists {
if node != nil {
heap.Push(h, node)
}
}
dummy := &ListNode{Val: -1}
cur := dummy
for h.Len() > 0 {
minNode := heap.Pop(h).(*ListNode)
cur.Next = minNode
cur = cur.Next
if minNode.Next != nil {
heap.Push(h, minNode.Next)
}
}
return dummy.Next
}
2.两数相加
给你两个非空的链表,表示两个非负的整数。它们每位数字都是按照逆序的方式存储的,并且每个节点只能存储一位数字。请你将两个数相加,并以相同形式返回一个表示和的链表。你可以假设除了数字0之外,这两个数都不会以0开头。
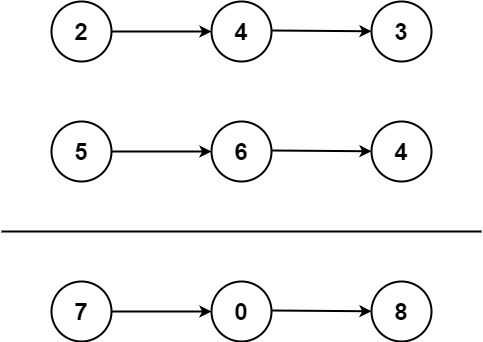
解题思路
可以逐位进行相加并处理进位。步骤如下:
初始化一个虚拟头节点
dummy和一个指针cur,用于构建相加后的链表。同时,初始化一个变量carry用于存储进位值,初始值为 0。当两个链表中有一个还有节点未处理时,执行以下操作:
- 获取链表当前节点的值,如果链表已经遍历完,可以认为其值为 0。
- 计算两个节点值之和以及进位值,更新进位值
carry。 - 创建一个新的节点,其值为节点值之和取模 10 的结果,将新节点加入相加后的链表,并更新指针
cur。 - 更新两个链表的当前节点,指向下一个节点。
当两个链表都遍历完后,检查进位值
carry是否大于 0,如果大于 0,说明还有一个进位需要处理,创建一个值为carry的节点并加入相加后的链表。返回虚拟头节点的下一个节点,即为相加后的链表头节点。
/**
* Definition for singly-linked list.
* struct ListNode {
* int val;
* ListNode *next;
* ListNode() : val(0), next(nullptr) {}
* ListNode(int x) : val(x), next(nullptr) {}
* ListNode(int x, ListNode *next) : val(x), next(next) {}
* };
*/
class Solution {
public:
ListNode* addTwoNumbers(ListNode* l1, ListNode* l2) {
ListNode dummy(-1);
ListNode* cur = &dummy;
int carry = 0;
while(l1 || l2 || carry) {
int val1 = l1 ? l1->val : 0;
int val2 = l2 ? l2->val : 0;
int sum = val1 + val2 + carry;
carry = sum / 10;
cur->next = new ListNode(sum % 10);
cur = cur->next;
if(l1) l1 = l1->next;
if(l2) l2 = l2->next;
}
return dummy.next;
}
};
/**
* Definition for singly-linked list.
* public class ListNode {
* int val;
* ListNode next;
* ListNode(int x) { val = x; }
* }
*/
class Solution {
public ListNode addTwoNumbers(ListNode l1, ListNode l2) {
ListNode dummy = new ListNode(-1);
ListNode cur = dummy;
int carry = 0;
while(l1 != null || l2 != null || carry != 0) {
int val1 = l1 != null ? l1.val : 0;
int val2 = l2 != null ? l2.val : 0;
int sum = val1 + val2 + carry;
carry = sum / 10;
cur.next = new ListNode(sum % 10);
cur = cur.next;
if(l1 != null) l1 = l1.next;
if(l2 != null) l2 = l2.next;
}
return dummy.next;
}
}
/**
* Definition for singly-linked list.
* type ListNode struct {
* Val int
* Next *ListNode
* }
*/
func NewListNode(val int) *ListNode {
return &ListNode{Val: val, Next: nil}
}
func addTwoNumbers(l1 *ListNode, l2 *ListNode) *ListNode {
dummy := &ListNode{-1, nil}
cur := dummy
carry := 0
for l1 != nil || l2 != nil || carry != 0 {
val1 := 0
if l1 != nil {
val1 = l1.Val
l1 = l1.Next
}
val2 := 0
if l2 != nil {
val2 = l2.Val
l2 = l2.Next
}
sum := val1 + val2 + carry
carry = sum / 10
cur.Next = NewListNode(sum % 10)
cur = cur.Next
}
return dummy.Next
}
92.反转链表 II
给你单链表的头指针 head 和两个整数 left 和 right ,其中 left <= right 。请你反转从位置 left 到位置 right 的链表节点,返回 反转后的链表 。
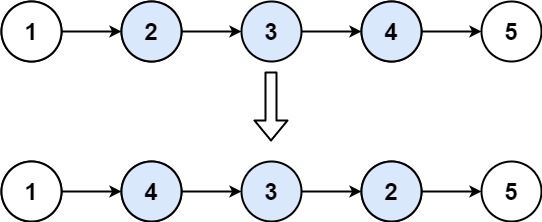
解题思路
要反转链表中指定位置的节点,可以先找到待反转部分的前一个节点和后一个节点,然后反转待反转部分,最后将前后节点与反转部分重新连接。以下是详细的步骤:
- 创建一个虚拟头节点
dummy,并创建一个指针cur指向虚拟头节点。这样可以处理需要反转的部分包含链表头节点的特殊情况。 - 将指针
cur向前移动left - 2步,找到待反转部分的前一个节点(如果left等于 1,则cur仍指向虚拟头节点)。 - 保存待反转部分的头节点
start和尾节点end。将指针end向前移动right - left步,找到待反转部分的最后一个节点。 - 将待反转部分的后一个节点
next保存为end.next。 - 反转待反转部分,可以使用迭代或递归方法。将反转后的部分的头节点返回。
- 更新指针
cur.next和start.next,将反转后的部分与前后节点重新连接。 - 返回虚拟头节点的下一个节点,即为反转后的链表头节点。
class Solution {
public:
ListNode* reverseBetween(ListNode* head, int left, int right) {
ListNode dummy(-1);
dummy.next = head;
ListNode* cur = &dummy;
for (int i = 1; i < left; ++i) {
cur = cur->next;
}
ListNode* start = cur->next;
ListNode* end = cur->next;
for (int i = left; i < right; ++i) {
end = end->next;
}
ListNode* next = end->next;
end->next = nullptr;
cur->next = reverseList(start);
start->next = next;
return dummy.next;
}
ListNode* reverseList(ListNode* head) {
ListNode* prev = nullptr;
ListNode* cur = head;
while (cur) {
ListNode* next = cur->next;
cur->next = prev;
prev = cur;
cur = next;
}
return prev;
}
};
/**
* Definition for singly-linked list.
* public class ListNode {
* int val;
* ListNode next;
* ListNode() {}
* ListNode(int val) { this.val = val; }
* ListNode(int val, ListNode next) { this.val = val; this.next = next; }
* }
*/
class Solution {
public ListNode reverseBetween(ListNode head, int left, int right) {
ListNode dummy = new ListNode(-1);
dummy.next = head;
ListNode cur = dummy;
for (int i = 1; i < left; ++i) {
cur = cur.next;
}
ListNode start = cur.next;
ListNode end = cur.next;
for (int i = left; i < right; ++i) {
end = end.next;
}
ListNode next = end.next;
end.next = null;
cur.next = reverseList(start);
start.next = next;
return dummy.next;
}
public ListNode reverseList(ListNode head) {
ListNode prev = null;
ListNode cur = head;
while (cur != null) {
ListNode next = cur.next;
cur.next = prev;
prev = cur;
cur = next;
}
return prev;
}
}
func reverseBetween(head *ListNode, left int, right int) *ListNode {
dummy := &ListNode{-1, head}
cur := dummy
for i := 1; i < left; i++ {
cur = cur.Next
}
start := cur.Next
end := cur.Next
for i := left; i < right; i++ {
end = end.Next
}
next := end.Next
end.Next = nil
cur.Next = reverseList(start)
start.Next = next
return dummy.Next
}
func reverseList(head *ListNode) *ListNode {
var prev *ListNode
cur := head
for cur != nil {
next := cur.Next
cur.Next = prev
prev = cur
cur = next
}
return prev
}
142.环形链表 II
给定一个链表的头节点
head,返回链表开始入环的第一个节点。 如果链表无环,则返回null。

解题思路
快慢指针的思路如下,建议直接记住做法。
- 首先,检查输入的链表是否为空,或者只有一个元素。如果满足这两个条件之一,直接返回 nullptr,因为这种情况下链表中不可能存在环。
- 定义两个指针,
fast和slow,都初始化为指向链表头结点。fast指针每次移动两个节点,slow指针每次移动一个节点。 - 在一个循环中,同时移动
fast和slow指针。如果链表中存在环,fast和slow指针最终会相遇。如果在移动过程中,fast指针遇到了空节点,说明链表没有环,此时返回 nullptr。 - 当
fast和slow相遇时,说明链表中存在环。为了找到环的起始节点,将fast指针重新指向链表头结点,保持slow指针不变。 - 再次开始一个循环,同时移动
fast和slow指针,但这次每次都只移动一个节点。当fast和slow再次相遇时,相遇点即为环的起始节点。 - 返回环的起始节点。
class Solution {
public:
ListNode* detectCycle(ListNode* head) {
if (!head || !head->next) {
return nullptr;
}
ListNode* fast = head;
ListNode* slow = head;
while (fast && fast->next) {
fast = fast->next->next;
slow = slow->next;
if (fast == slow) {
break;
}
}
if (fast != slow) {
return nullptr;
}
fast = head;
while (fast != slow) {
fast = fast->next;
slow = slow->next;
}
return slow;
}
};
/**
* Definition for singly-linked list.
* class ListNode {
* int val;
* ListNode next;
* ListNode(int x) {
* val = x;
* next = null;
* }
* }
*/
class Solution {
public ListNode detectCycle(ListNode head) {
if (head == null || head.next == null) {
return null;
}
ListNode fast = head;
ListNode slow = head;
while (fast != null && fast.next != null) {
fast = fast.next.next;
slow = slow.next;
if (fast == slow) {
break;
}
}
if (fast != slow) {
return null;
}
fast = head;
while (fast != slow) {
fast = fast.next;
slow = slow.next;
}
return slow;
}
}
func detectCycle(head *ListNode) *ListNode {
if head == nil || head.Next == nil {
return nil
}
fast := head
slow := head
for fast != nil && fast.Next != nil {
fast = fast.Next.Next
slow = slow.Next
if fast == slow {
break
}
}
if fast != slow {
return nil
}
fast = head
for fast != slow {
fast = fast.Next
slow = slow.Next
}
return slow
}
82.删除排序链表中的重复元素 II
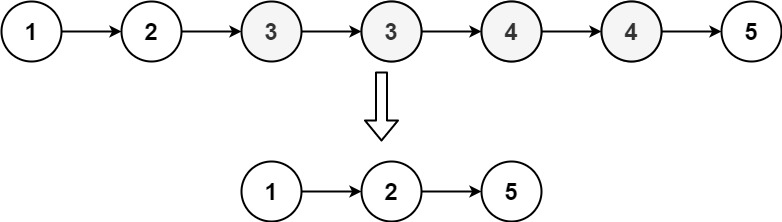
解题思路
使用一个辅助指针遍历链表,同时维护一个指针指向当前不重复节点的最后一个节点。以下是详细的步骤:
创建一个虚拟头节点
dummy,令dummy.next = head。这样可以简化对头节点的处理。初始化两个指针
prev和cur,分别指向虚拟头节点dummy和头节点head。遍历链表,直到
cur为None:使用一个循环,检查当前节点
cur和下一个节点cur.next是否具有相同的值。如果相同,将cur向前移动,跳过具有相同值的节点。如果
prev.next与cur不相等,说明prev.next和cur之间存在重复的节点,需要将这些重复节点删除。将prev.next指向cur.next,这样就跳过了这些重复节点。如果
prev.next与cur相等,说明当前节点不重复,将prev指向cur。移动
cur指针,指向下一个节点cur.next。
遍历结束后,返回
dummy.next,即为新链表的头节点。
class Solution {
public:
ListNode* deleteDuplicates(ListNode* head) {
ListNode* dummy = new ListNode(0, head);
ListNode* prev = dummy;
ListNode* cur = head;
while (cur) {
while (cur->next && cur->val == cur->next->val) {
cur = cur->next;
}
if (prev->next != cur) {
prev->next = cur->next;
} else {
prev = cur;
}
cur = cur->next;
}
return dummy->next;
}
};
/**
* Definition for singly-linked list.
* public class ListNode {
* int val;
* ListNode next;
* ListNode() {}
* ListNode(int val) { this.val = val; }
* ListNode(int val, ListNode next) { this.val = val; this.next = next; }
* }
*/
public class Solution {
public ListNode deleteDuplicates(ListNode head) {
ListNode dummy = new ListNode(0);
dummy.next = head;
ListNode prev = dummy;
ListNode cur = head;
while (cur != null) {
while (cur.next != null && cur.val == cur.next.val) {
cur = cur.next;
}
if (prev.next != cur) {
prev.next = cur.next;
} else {
prev = cur;
}
cur = cur.next;
}
return dummy.next;
}
}
/**
* Definition for singly-linked list.
* type ListNode struct {
* Val int
* Next *ListNode
* }
*/
func deleteDuplicates(head *ListNode) *ListNode {
dummy := &ListNode{0, head}
prev := dummy
cur := head
for cur != nil {
for cur.Next != nil && cur.Val == cur.Next.Val {
cur = cur.Next
}
if prev.Next != cur {
prev.Next = cur.Next
} else {
prev = cur
}
cur = cur.Next
}
return dummy.Next
}