链表必刷题第三部分
234. 回文链表
给你一个单链表的头节点
head,请你判断该链表是否为回文链表。如果是,返回true;否则,返回false。
解题思路
想做到时间复杂度O(n),空间复杂度O(1),那么就是先快慢指针找到中点,然后反转后半部分链表,然后比较一遍;如果链表个数是奇数的话,存在后边部分比前半部分多1的可能性,所以前后链表只要有一个遍历完了就退出比较;链表操作是很容易发生bug的地方,建议多创指针,然后每一步写的详细些,该断开的地方断开,这样不容易出错。具体实现步骤如下:
- 使用快慢指针法找到链表的中间节点,并将前半部分和后半部分分别保存到
begin1和begin2指针中。 - 反转后半部分链表,保存到
p2指针中,并将前半部分链表的最后一个节点指向p2。 - 比较前半部分链表和反转后的后半部分链表是否相同,如果不同则返回
false。 - 恢复后半部分链表的顺序。
- 返回
true。
class Solution {
public:
ListNode* reverse(ListNode* head) {
ListNode* prev = nullptr;
ListNode* curr = head;
while (curr) {
ListNode* next = curr->next;
curr->next = prev;
prev = curr;
curr = next;
}
return prev;
}
bool isPalindrome(ListNode* head) {
if (!head || !head->next) {
return true;
}
ListNode* slow = head;
ListNode* fast = head;
while (fast && fast->next) {
slow = slow->next;
fast = fast->next->next;
}
slow = reverse(slow);
ListNode* p1 = head;
ListNode* p2 = slow;
while (p1 && p2) {
if (p1->val != p2->val) {
return false;
}
p1 = p1->next;
p2 = p2->next;
}
return true;
}
};
/**
* Definition for singly-linked list.
* public class ListNode {
* int val;
* ListNode next;
* ListNode() {}
* ListNode(int val) { this.val = val; }
* ListNode(int val, ListNode next) { this.val = val; this.next = next; }
* }
*/
public class Solution {
public ListNode reverse(ListNode head) {
ListNode prev = null;
ListNode curr = head;
while (curr != null) {
ListNode next = curr.next;
curr.next = prev;
prev = curr;
curr = next;
}
return prev;
}
public boolean isPalindrome(ListNode head) {
if (head == null || head.next == null) {
return true;
}
ListNode slow = head;
ListNode fast = head;
while (fast != null && fast.next != null) {
slow = slow.next;
fast = fast.next.next;
}
slow = reverse(slow);
ListNode p1 = head;
ListNode p2 = slow;
while (p1 != null && p2 != null) {
if (p1.val != p2.val) {
return false;
}
p1 = p1.next;
p2 = p2.next;
}
return true;
}
}
func reverse(head *ListNode) *ListNode {
var prev *ListNode
curr := head
for curr != nil {
next := curr.Next
curr.Next = prev
prev = curr
curr = next
}
return prev
}
func isPalindrome(head *ListNode) bool {
if head == nil || head.Next == nil {
return true
}
slow := head
fast := head
for fast != nil && fast.Next != nil {
slow = slow.Next
fast = fast.Next.Next
}
slow = reverse(slow)
p1 := head
p2 := slow
for p1 != nil && p2 != nil {
if p1.Val != p2.Val {
return false
}
p1 = p1.Next
p2 = p2.Next
}
return true
}
24. 两两交换链表中的节点
给你一个链表,两两交换其中相邻的节点,并返回交换后链表的头节点。你必须在不修改节点内部的值的情况下完成本题(即,只能进行节点交换)。
解题思路
这道题也是一个考察链表操作的问题,两两交换节点就是以3个为一组进行操作,当剩下节点不足三个时,直接返回。链表操作中很多节点连接关系不注意就变化了,可以先把每个操作的节点存下来,这样不容易出错。具体操作如下:
首先检查链表是否为空或只有一个元素,如果满足这些条件,则不需要进行任何交换,直接返回链表头节点。
创建一个虚拟头节点
dummy,并将其next指针指向链表头节点。这样可以简化对头节点的处理。初始化一个指针
cur,指向虚拟头节点。用于遍历链表。使用一个循环来遍历链表,直到
cur的下一个节点或下下个节点为空,表示已经处理完链表中的所有节点对。- 在循环内部,首先记录两个相邻节点的指针:
even指向当前cur的下一个节点,odd指向当前cur的下下个节点。这里,我们需要交换even和odd指向的节点。 - 更新
even节点的next指针,使其指向odd节点的下一个节点。 - 更新
cur的next指针,使其指向odd节点。 - 更新
odd节点的next指针,使其指向even节点。 - 将
cur指针移动到even节点。因为even节点已经交换到了下一个节点对的前面,所以移动到这个位置准备处理下一个节点对。
- 在循环内部,首先记录两个相邻节点的指针:
循环结束后,返回虚拟头节点
dummy的next指针,即新链表的头节点。
/**
* Definition for singly-linked list.
* struct ListNode {
* int val;
* ListNode *next;
* ListNode() : val(0), next(nullptr) {}
* ListNode(int x) : val(x), next(nullptr) {}
* ListNode(int x, ListNode *next) : val(x), next(next) {}
* };
*/
class Solution {
public:
ListNode* swapPairs(ListNode* head) {
if (!head || !head->next) {
return head;
}
ListNode* dummy = new ListNode(0, head);
ListNode* cur = dummy;
while (cur->next && cur->next->next) {
ListNode* even = cur->next;
ListNode* odd = cur->next->next;
even->next = odd->next;
cur->next = odd;
odd->next = even;
cur = even;
}
return dummy->next;
}
};
/*
// Definition for a Node.
class Node {
int val;
Node next;
Node random;
public Node(int val) {
this.val = val;
this.next = null;
this.random = null;
}
}
*/
public class Solution {
public ListNode swapPairs(ListNode head) {
if (head == null || head.next == null) {
return head;
}
ListNode dummy = new ListNode(0);
dummy.next = head;
ListNode cur = dummy;
while (cur.next != null && cur.next.next != null) {
ListNode even = cur.next;
ListNode odd = cur.next.next;
even.next = odd.next;
cur.next = odd;
odd.next = even;
cur = even;
}
return dummy.next;
}
}
func swapPairs(head *ListNode) *ListNode {
if head == nil || head.Next == nil {
return head
}
dummy := &ListNode{0, head}
cur := dummy
for cur.Next != nil && cur.Next.Next != nil {
even := cur.Next
odd := cur.Next.Next
even.Next = odd.Next
cur.Next = odd
odd.Next = even
cur = even
}
return dummy.Next
}
445. 两数相加 II
给你两个 非空 链表来代表两个非负整数。数字最高位位于链表开始位置。它们的每个节点只存储一位数字。将这两数相加会返回一个新的链表。
你可以假设除了数字 0 之外,这两个数字都不会以零开头。
解题思路
正常思路是反转链表变成两数相加问题,如果题目要求不能反转链表的话,可以用栈或者递归代替反转链表。
定义一个
reverseNode函数,用于反转链表。这个函数接受一个链表头节点cur,并返回反转后链表的头节点。在这个函数中,我们使用三个指针pre、cur和next,以便在反转过程中始终保持对链表的正确连接。在
addTwoNumbers函数中,我们首先创建一个虚拟头节点org和一个当前节点指针cur,用于构建结果链表。我们还需要一个变量carry用于存储进位值。然后,我们分别反转输入链表
l1和l2,使其表示的数字变为正序。接下来,我们遍历两个反转后的链表
l1和l2。在每次迭代中,我们分别从两个链表中获取节点值val1和val2,并将它们与进位值carry相加。计算新的进位值carry以及当前节点的值sumVal % 10。为当前和创建一个新的节点,并将其添加到结果链表中。然后,移动
l1和l2的指针到下一个节点,直到它们都为nullptr且没有进位值。最后,我们再次反转结果链表
org->next,将其变回倒序表示的数字,并返回这个反转后的链表头节点作为最终结果。
class Solution {
public:
ListNode* reverseNode(ListNode* cur) {
ListNode* pre = nullptr, *next = nullptr;
while (cur != nullptr) {
next = cur->next;
cur->next = pre;
pre = cur;
cur = next;
}
return pre;
}
ListNode* addTwoNumbers(ListNode* l1, ListNode* l2) {
ListNode* org = new ListNode(-1);
ListNode* cur = org;
int carry = 0;
l1 = reverseNode(l1);
l2 = reverseNode(l2);
while (l1 || l2 || carry) {
int val1 = l1 ? l1->val : 0;
int val2 = l2 ? l2->val : 0;
int sumVal = val1 + val2 + carry;
carry = sumVal / 10;
cur->next = new ListNode(sumVal % 10);
cur = cur->next;
if (l1) l1 = l1->next;
if (l2) l2 = l2->next;
}
ListNode* ans = reverseNode(org->next);
return ans;
}
};
public class Solution {
public ListNode reverseNode(ListNode cur) {
ListNode pre = null, next = null;
while (cur != null) {
next = cur.next;
cur.next = pre;
pre = cur;
cur = next;
}
return pre;
}
public ListNode addTwoNumbers(ListNode l1, ListNode l2) {
ListNode org = new ListNode(-1);
ListNode cur = org;
int carry = 0;
l1 = reverseNode(l1);
l2 = reverseNode(l2);
while (l1 != null || l2 != null || carry != 0) {
int val1 = l1 != null ? l1.val : 0;
int val2 = l2 != null ? l2.val : 0;
int sumVal = val1 + val2 + carry;
carry = sumVal / 10;
cur.next = new ListNode(sumVal % 10);
cur = cur.next;
if (l1 != null) l1 = l1.next;
if (l2 != null) l2 = l2.next;
}
ListNode ans = reverseNode(org.next);
return ans;
}
}
func reverseNode(cur *ListNode) *ListNode {
var pre, next *ListNode
for cur != nil {
next = cur.Next
cur.Next = pre
pre = cur
cur = next
}
return pre
}
func addTwoNumbers(l1, l2 *ListNode) *ListNode {
org := &ListNode{-1, nil}
cur := org
carry := 0
l1 = reverseNode(l1)
l2 = reverseNode(l2)
for l1 != nil || l2 != nil || carry != 0 {
val1 := 0
if l1 != nil {
val1 = l1.Val
l1 = l1.Next
}
val2 := 0
if l2 != nil {
val2 = l2.Val
l2 = l2.Next
}
sumVal := val1 + val2 + carry
carry = sumVal / 10
cur.Next = &ListNode{Val: sumVal % 10, Next: nil}
cur = cur.Next
}
ans := reverseNode(org.Next)
return ans
}
61. 旋转链表
给你一个链表的头节点
head,旋转链表,将链表每个节点向右移动k个位置。
解题思路
- 特殊情况处理:如果链表为空(
!head)或者 k 为 0,直接返回链表头节点,因为不需要进行旋转操作。 - 获取链表长度和尾节点:遍历整个链表,获取链表的长度(
count)并找到链表的尾节点(end)。 - 计算实际旋转次数:因为当旋转次数等于链表长度时,链表恢复原状,所以我们只需要计算实际需要旋转的次数
rotateTime,即k % count。 - 判断是否需要旋转:如果实际旋转次数等于 0,说明不需要进行旋转操作,直接返回链表头节点。
- 连接链表尾部和头部:将链表尾部(
end)的 next 指针指向链表头部(head),形成一个循环链表。 - 寻找新的链表尾部:根据实际旋转次数
rotateTime,计算新的链表尾部(newTail)的位置。从链表头部开始,遍历到新的链表尾部。 - 断开新的链表尾部与链表头部之间的连接:将新的链表尾部(
newTail)的 next 指针置为 nullptr,同时更新链表头节点(head)为新的链表尾部的下一个节点。 - 返回新的链表头节点。
/**
* Definition for singly-linked list.
* struct ListNode {
* int val;
* ListNode *next;
* ListNode() : val(0), next(nullptr) {}
* ListNode(int x) : val(x), next(nullptr) {}
* ListNode(int x, ListNode *next) : val(x), next(next) {}
* };
*/
/**
* Definition for singly-linked list.
* struct ListNode {
* int val;
* ListNode *next;
* ListNode() : val(0), next(nullptr) {}
* ListNode(int x) : val(x), next(nullptr) {}
* ListNode(int x, ListNode *next) : val(x), next(next) {}
* };
*/
class Solution {
public:
ListNode* rotateRight(ListNode* head, int k) {
if (!head || k == 0) return head;
int count = 1;
ListNode* end = head;
while (end->next) {
end = end->next;
count++;
}
int rotateTime = k % count;
if (rotateTime == 0) return head;
end->next = head;
int newTailPos = count - rotateTime;
ListNode* newTail = head;
for (int i = 1; i < newTailPos; i++) {
newTail = newTail->next;
}
head = newTail->next;
newTail->next = nullptr;
return head;
}
};
/*
* Definition for singly-linked list.
* public class ListNode {
* int val;
* ListNode next;
* ListNode() {}
* ListNode(int val) { this.val = val; }
* ListNode(int val, ListNode next) { this.val = val; this.next = next; }
* }
*/
class Solution {
public ListNode rotateRight(ListNode head, int k) {
if (head == null || k == 0) return head;
int count = 1;
ListNode end = head;
while (end.next != null) {
end = end.next;
count++;
}
int rotateTime = k % count;
if (rotateTime == 0) return head;
end.next = head;
int newTailPos = count - rotateTime;
ListNode newTail = head;
for (int i = 1; i < newTailPos; i++) {
newTail = newTail.next;
}
head = newTail.next;
newTail.next = null;
return head;
}
}
func rotateRight(head *ListNode, k int) *ListNode {
if head == nil || k == 0 {
return head
}
count := 1
end := head
for end.Next != nil {
end = end.Next
count++
}
rotateTime := k % count
if rotateTime == 0 {
return head
}
end.Next = head
newTailPos := count - rotateTime
newTail := head
for i := 1; i < newTailPos; i++ {
newTail = newTail.Next
}
head = newTail.Next
newTail.Next = nil
return head
}
328. 奇偶链表
给定单链表的头节点 head ,将所有索引为奇数的节点和索引为偶数的节点分别组合在一起,然后返回重新排序的列表。第一个节点的索引被认为是 奇数 , 第二个节点的索引为 偶数 ,以此类推。请注意,偶数组和奇数组内部的相对顺序应该与输入时保持一致。
你必须在 O(1) 的额外空间复杂度和 O(n) 的时间复杂度下解决这个问题。
解题思路
- 特殊情况处理:如果链表为空,直接返回空指针。
- 初始化指针:使用两个指针
odd和even分别指向链表的第一个节点(奇数头节点)和第二个节点(偶数头节点)。同时,用一个额外的指针evenHead保存偶数头节点的位置,以便最后将奇数节点的尾部与偶数节点的头部相连。 - 遍历链表:使用一个循环遍历链表,直到
even节点为空或even->next节点为空。在每次循环中,我们将当前的奇数节点odd的next指针指向下一个奇数节点(即odd->next->next),并将当前的偶数节点even的next指针指向下一个偶数节点(即even->next->next)。然后更新odd和even节点为它们的下一个奇数节点和偶数节点。 - 连接奇数节点和偶数节点:当遍历完成后,奇数节点的尾部和偶数节点的头部还没有连接。将奇数节点的尾部(
odd)的next指针指向偶数头节点(evenHead)。 - 返回结果:返回链表的头节点(
head),此时链表已经将奇数位置的节点和偶数位置的节点分离。
class Solution {
public:
ListNode* oddEvenList(ListNode* head) {
if (head == nullptr) return nullptr;
ListNode* odd = head;
ListNode* even = head->next;
ListNode* evenHead = even;
while (even != nullptr && even->next != nullptr) {
odd->next = odd->next->next;
even->next = even->next->next;
odd = odd->next;
even = even->next;
}
odd->next = evenHead;
return head;
}
};
/*
* Definition for singly-linked list.
* public class ListNode {
* int val;
* ListNode next;
* ListNode() {}
* ListNode(int val) { this.val = val; }
* ListNode(int val, ListNode next) { this.val = val; this.next = next; }
* }
*/
class Solution {
public ListNode oddEvenList(ListNode head) {
if (head == null) return null;
ListNode odd = head;
ListNode even = head.next;
ListNode evenHead = even;
while (even != null && even.next != null) {
odd.next = odd.next.next;
even.next = even.next.next;
odd = odd.next;
even = even.next;
}
odd.next = evenHead;
return head;
}
}
func oddEvenList(head *ListNode) *ListNode {
if head == nil {
return nil
}
odd := head
even := head.Next
evenHead := even
for even != nil && even.Next != nil {
odd.Next = odd.Next.Next
even.Next = even.Next.Next
odd = odd.Next
even = even.Next
}
odd.Next = evenHead
return head
}
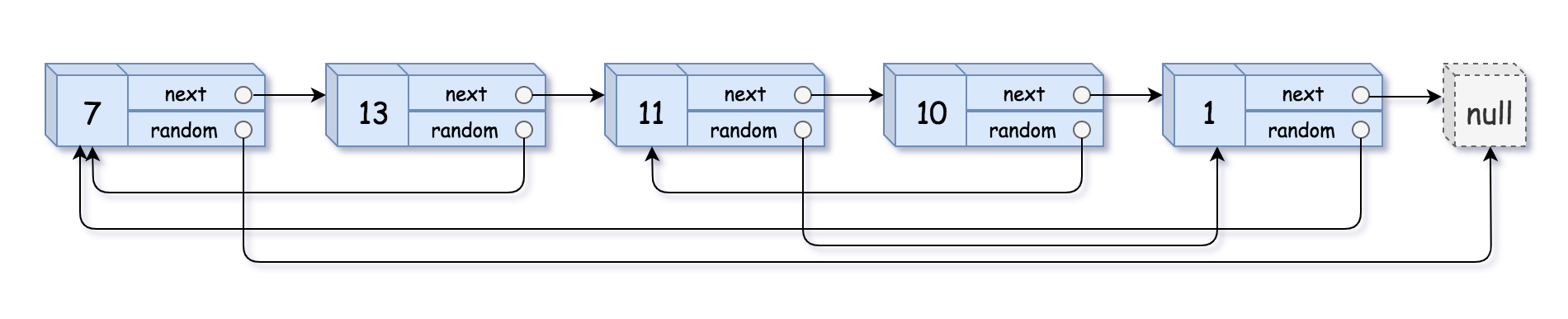
138. 复制带随机指针的链表
给你一个长度为 n 的链表,每个节点包含一个额外增加的随机指针 random ,该指针可以指向链表中的任何节点或空节点。
构造这个链表的 深拷贝。 深拷贝应该正好由 n 个 全新 节点组成,其中每个新节点的值都设为其对应的原节点的值。新节点的 next 指针和 random 指针也都应指向复制链表中的新节点,并使原链表和复制链表中的这些指针能够表示相同的链表状态。复制链表中的指针都不应指向原链表中的节点 。例如,如果原链表中有 X 和 Y 两个节点,其中 X.random --> Y 。那么在复制链表中对应的两个节点 x 和 y ,同样有 x.random --> y 。
返回复制链表的头节点。
用一个由 n 个节点组成的链表来表示输入/输出中的链表。每个节点用一个 [val, random_index] 表示:
解题思路一:额外创建一个hash表
按next顺序遍历给出的链表,并为每个旧节点创建一个新节点,用hash表存映射,之后在给每个新节点建立连接关系,旧节点->旧节点的映射关系拷贝到新节点上就是hash[旧节点]->hash[旧节点],next和random的建立方式相同,遍历每个旧节点即可。具体操作如下:
创建一个哈希表(unordered_map)用于存储原始链表节点到新链表节点的映射关系。
遍历原始链表,执行以下操作:
a. 创建一个新节点 temp,值为当前节点的值。
b. 在哈希表中存储原始节点到新节点的映射关系,即 hash[cur] = temp。
c. 将原始链表的当前指针 cur 移动到下一个节点。
当第一次遍历完成后,再次遍历原始链表,执行以下操作:
a. 将新链表中当前节点的 next 指针指向原始链表中当前节点的 next 指针所指向的节点在哈希表中对应的新节点,即 hash[cur]->next = hash[cur->next]。
b. 将新链表中当前节点的 random 指针指向原始链表中当前节点的 random 指针所指向的节点在哈希表中对应的新节点,即 hash[cur]->random = hash[cur->random]。
c. 将原始链表的当前指针 cur 移动到下一个节点。
返回新链表的头节点,即 hash[head]。
解题思路二:不需要用hash表来存映射关系,空间复杂度较低,但是对链表操作要求比较高。
创建新节点并插入到原链表中:遍历原链表,在每个节点后面创建一个新节点,新节点的值与原节点相同,新节点的 next 指针指向原节点的下一个节点。
设置新节点的 random 指针:再次遍历原链表,如果原节点的 random 指针不为空,则将新节点的 random 指针设置为原节点 random 指针所指向节点的下一个节点。
分离新链表和原链表:最后一次遍历原链表,将原链表和新链表分离,同时更新新链表的 next 指针。
// 方法一,hash表存映射
class Solution {
public:
Node* copyRandomList(Node* head) {
unordered_map<Node*,Node*> hash;
Node* cur=head;
while(cur!=nullptr){
Node* temp=new Node(cur->val);
hash[cur]=temp;
cur=cur->next;
}
cur=head;
while(cur!=nullptr){
hash[cur]->next=hash[cur->next];
hash[cur]->random=hash[cur->random];
cur=cur->next;
}
return hash[head];
}
};
// 方法二,新节点挂旧节点后面
class Solution {
public:
Node* copyRandomList(Node* head) {
if (head == nullptr) return nullptr;
Node* cur = head;
// 创建新节点并插入到原链表中
while (cur != nullptr) {
Node* newNode = new Node(cur->val);
newNode->next = cur->next;
cur->next = newNode;
cur = newNode->next;
}
// 设置新节点的 random 指针
cur = head;
while (cur != nullptr) {
if (cur->random != nullptr) {
cur->next->random = cur->random->next;
}
cur = cur->next->next;
}
// 分离新链表和原链表
cur = head;
Node* newHead = head->next;
Node* newCur = newHead;
while (cur != nullptr) {
cur->next = cur->next->next;
if (newCur->next != nullptr) {
newCur->next = newCur->next->next;
}
cur = cur->next;
newCur = newCur->next;
}
return newHead;
}
};
// 方法一,hash表存映射
class Solution {
public Node copyRandomList(Node head) {
Map<Node, Node> map = new HashMap<>();
Node cur = head;
while (cur != null) {
map.put(cur, new Node(cur.val));
cur = cur.next;
}
cur = head;
while (cur != null) {
map.get(cur).next = map.get(cur.next);
map.get(cur).random = map.get(cur.random);
cur = cur.next;
}
return map.get(head);
}
}
// 方法二,新节点挂旧节点后面
class Solution {
public Node copyRandomList(Node head) {
if (head == null) return null;
Node cur = head;
// 创建新节点并插入到原链表中
while (cur != null) {
Node newNode = new Node(cur.val);
newNode.next = cur.next;
cur.next = newNode;
cur = newNode.next;
}
// 设置新节点的 random 指针
cur = head;
while (cur != null) {
if (cur.random != null) {
cur.next.random = cur.random.next;
}
cur = cur.next.next;
}
// 分离新链表和原链表
cur = head;
Node newHead = head.next;
Node newCur = newHead;
while (cur != null) {
cur.next = cur.next.next;
if (newCur.next != null) {
newCur.next = newCur.next.next;
}
cur = cur.next;
newCur = newCur.next;
}
return newHead;
}
}
// 方法一,hash表存映射
func copyRandomList(head *Node) *Node {
hash := make(map[*Node]*Node)
cur := head
for cur != nil {
temp := &Node{Val: cur.Val}
hash[cur] = temp
cur = cur.Next
}
cur = head
for cur != nil {
hash[cur].Next = hash[cur.Next]
hash[cur].Random = hash[cur.Random]
cur = cur.Next
}
return hash[head]
}
// 方法二,新节点挂旧节点后面
func copyRandomList(head *Node) *Node {
if head == nil {
return nil
}
cur := head
// 创建新节点并插入到原链表中
for cur != nil {
newNode := &Node{Val: cur.Val}
newNode.Next = cur.Next
cur.Next = newNode
cur = newNode.Next
}
// 设置新节点的 random 指针
cur = head
for cur != nil {
if cur.Random != nil {
cur.Next.Random = cur.Random.Next
}
cur = cur.Next.Next
}
// 分离新链表和原链表
cur = head
newHead := head.Next
newCur := newHead
for cur != nil {
cur.Next = cur.Next.Next
if newCur.Next != nil {
newCur.Next = newCur.Next.Next
}
cur = cur.Next
newCur = newCur.Next
}
return newHead
}