树必刷题第三部分
124. 二叉树中的最大路径和
路径 被定义为一条从树中任意节点出发,沿父节点-子节点连接,达到任意节点的序列。同一个节点在一条路径序列中 至多出现一次 。该路径 至少包含一个 节点,且不一定经过根节点。路径和 是路径中各节点值的总和。
给你一个二叉树的根节点 root ,返回其最大路径和 。
解题思路
定义一个变量ans,初始值为整数最小值(INT_MIN)。这个变量用于存储计算过程中的最大路径和。具体步骤如下:
- 如果节点为空(
node == nullptr),则返回0。 - 递归地计算左子树和右子树的最大子路径和(
left和right)。 - 计算当前节点的最大子树和(
maxSubtreeSum),它等于当前节点的值加上左右子树最大子路径和中的最大值,与0比较取最大值。 - 计算经过当前节点的最大路径和(
maxPathSum),它等于当前节点的值加上左子树的非负最大子路径和和右子树的非负最大子路径和。 - 更新全局最大路径和(
ans)为ans和maxPathSum中的较大值。 - 最后返回当前节点的最大子树和(
maxSubtreeSum)。
对整棵树调用dfs函数,最终返回全局最大路径和(ans)。
/**
* Definition for a binary tree node.
* struct TreeNode {
* int val;
* TreeNode *left;
* TreeNode *right;
* TreeNode() : val(0), left(nullptr), right(nullptr) {}
* TreeNode(int x) : val(x), left(nullptr), right(nullptr) {}
* TreeNode(int x, TreeNode *left, TreeNode *right) : val(x), left(left), right(right) {}
* };
*/
class Solution {
public:
int maxPathSum(TreeNode* root) {
int ans = INT_MIN;
function<int(TreeNode*)> dfs = [&](TreeNode* node) -> int {
if (node == nullptr) {
return 0;
}
int left = dfs(node->left);
int right = dfs(node->right);
int maxSubtreeSum = max({left, right, 0}) + node->val;
int maxPathSum = node->val + max({left, 0}) + max({right, 0});
ans = max(ans, maxPathSum);
return maxSubtreeSum;
};
dfs(root);
return ans;
}
};
public class Solution {
private int ans = Integer.MIN_VALUE;
public int maxPathSum(TreeNode root) {
dfs(root);
return ans;
}
private int dfs(TreeNode node) {
if (node == null) {
return 0;
}
int left = dfs(node.left);
int right = dfs(node.right);
int maxSubtreeSum = Math.max(Math.max(left, right), 0) + node.val;
int maxPathSum = node.val + Math.max(left, 0) + Math.max(right, 0);
ans = Math.max(ans, maxPathSum);
return maxSubtreeSum;
}
}
func maxPathSum(root *TreeNode) int {
ans := math.MinInt32
var dfs func(*TreeNode) int
dfs = func(node *TreeNode) int {
if node == nil {
return 0
}
left := dfs(node.Left)
right := dfs(node.Right)
maxSubtreeSum := max(max(left, right)+node.Val, 0)
maxPathSum := node.Val + max(left, 0) + max(right, 0)
ans = max(ans, maxPathSum)
return maxSubtreeSum
}
dfs(root)
return ans
}
func max(x, y int) int {
if x > y {
return x
}
return y
}
543. 二叉树的直径
给定一棵二叉树,你需要计算它的直径长度。一棵二叉树的直径长度是任意两个结点路径长度中的最大值。这条路径可能穿过也可能不穿过根结点。

解题思路
对于每个节点来说,经过当前节点的直径长度,就是左右节点的深度减去两倍当前节点的深度,这就是当前节点的直径长度;用树形dp的方法获取到左右子树的深度,算出当前节点的直径长度,然后取所有节点中最大的直径长度。以下是具体操作:
定义一个变量
ans存储最长路径的节点数,初始值为 0。定义一个辅助函数
scan,参数为当前节点root和当前节点的深度depth。a. 如果当前节点为空,返回
depth - 1,因为它的父节点才是叶子节点。b. 递归计算当前节点左子树的最大深度
left。c. 递归计算当前节点右子树的最大深度
right。d. 更新最长路径的节点数
ans,使其为当前最长路径节点数与left + right - 2 * depth的较大值。e. 返回当前子树的最大深度,即
max(left, right)。调用辅助函数
scan,参数为根节点和初始深度 0。返回最长路径的节点数
ans。
/**
* Definition for a binary tree node.
* struct TreeNode {
* int val;
* TreeNode *left;
* TreeNode *right;
* TreeNode() : val(0), left(nullptr), right(nullptr) {}
* TreeNode(int x) : val(x), left(nullptr), right(nullptr) {}
* TreeNode(int x, TreeNode *left, TreeNode *right) : val(x), left(left), right(right) {}
* };
*/
class Solution {
private:
int ans=0;
int scan(TreeNode* root,int depth){
if(root==nullptr) return depth-1;//返回-1是因为它的父节点才是叶子
int left=scan(root->left,depth+1);
int right=scan(root->right,depth+1);
ans=max(ans,left+right-2*depth);
return max(left,right);
}
public:
int diameterOfBinaryTree(TreeNode* root) {
ans=0;
int n=scan(root,0);
return ans;
}
};
/**
* Definition for a binary tree node.
* public class TreeNode {
* int val;
* TreeNode left;
* TreeNode right;
* TreeNode() {}
* TreeNode(int val) { this.val = val; }
* TreeNode(int val, TreeNode left, TreeNode right) {
* this.val = val;
* this.left = left;
* this.right = right;
* }
* }
*/
class Solution {
private int ans = 0;
private int scan(TreeNode root, int depth) {
if (root == null) return depth - 1;
int left = scan(root.left, depth + 1);
int right = scan(root.right, depth + 1);
ans = Math.max(ans, left + right - 2 * depth);
return Math.max(left, right);
}
public int diameterOfBinaryTree(TreeNode root) {
ans = 0;
int n = scan(root, 0);
return ans;
}
}
func diameterOfBinaryTree(root *TreeNode) int {
ans := 0
var scan func(root *TreeNode, depth int) int
scan = func(root *TreeNode, depth int) int {
if root == nil {
return depth - 1
}
left := scan(root.Left, depth+1)
right := scan(root.Right, depth+1)
ans = max(ans, left+right-2*depth)
return max(left, right)
}
scan(root, 0)
return ans
}
func max(a, b int) int {
if a > b {
return a
}
return b
}
236. 二叉树的最近公共祖先
给定一个二叉树, 找到该树中两个指定节点的最近公共祖先。

解题思路
首先,检查当前节点(root)是否为 nullptr,如果是,说明已经到达了树的底部,返回 nullptr。
如果当前节点(root)等于 p 或 q 中的任何一个,说明找到了其中一个节点,返回当前节点。
递归地在左子树中查找 p 和 q 的最近公共祖先。将结果存储在
left变量中。递归地在右子树中查找 p 和 q 的最近公共祖先。将结果存储在
right变量中。如果
left和right均不为 nullptr,说明 p 和 q 分别位于当前节点(root)的左右子树中,因此当前节点就是它们的最近公共祖先。返回当前节点。如果
left不为 nullptr,而right为 nullptr,说明 p 和 q 的最近公共祖先在左子树中。返回left。如果
right不为 nullptr,而left为 nullptr,说明 p 和 q 的最近公共祖先在右子树中。返回right。如果上述所有条件均不满足,说明当前节点不是 p 和 q 的最近公共祖先。返回 nullptr。
class Solution {
public:
TreeNode* lowestCommonAncestor(TreeNode* root, TreeNode* p, TreeNode* q) {
if(root == nullptr) return nullptr;
if(root == p || root == q) return root;
TreeNode* left = lowestCommonAncestor(root->left, p, q);
TreeNode* right = lowestCommonAncestor(root->right, p, q);
if(left != nullptr && right != nullptr) return root;
if(left != nullptr) return left;
if(right != nullptr) return right;
return nullptr;
}
};
/**
* Definition for a binary tree node.
* public class TreeNode {
* int val;
* TreeNode left;
* TreeNode right;
* TreeNode(int x) { val = x; }
* }
*/
class Solution {
public TreeNode lowestCommonAncestor(TreeNode root, TreeNode p, TreeNode q) {
if(root == null) return null;
if(root == p || root == q) return root;
TreeNode left = lowestCommonAncestor(root.left, p, q);
TreeNode right = lowestCommonAncestor(root.right, p, q);
if(left != null && right != null) return root;
return (left != null) ? left : right;
}
}
/**
* Definition for a binary tree node.
* type TreeNode struct {
* Val int
* Left *TreeNode
* Right *TreeNode
* }
*/
func lowestCommonAncestor(root, p, q *TreeNode) *TreeNode {
if root == nil {
return nil
}
if root == p || root == q {
return root
}
left := lowestCommonAncestor(root.Left, p, q)
right := lowestCommonAncestor(root.Right, p, q)
if left != nil && right != nil {
return root
}
if left != nil {
return left
}
return right
}
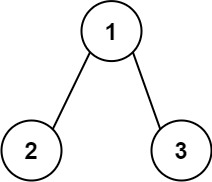
129. 求根节点到叶节点数字之和
给你一个二叉树的根节点 root ,树中每个节点都存放有一个 0 到 9 之间的数字。 每条从根节点到叶节点的路径都代表一个数字:
例如,从根节点到叶节点的路径 1 -> 2 -> 3 表示数字 123 。 计算从根节点到叶节点生成的 所有数字之和 。
/**
* Definition for a binary tree node.
* public class TreeNode {
* int val;
* TreeNode left;
* TreeNode right;
* TreeNode() {}
* TreeNode(int val) { this.val = val; }
* TreeNode(int val, TreeNode left, TreeNode right) {
* this.val = val;
* this.left = left;
* this.right = right;
* }
* }
*/
class Solution {
private int res;
public int sumNumbers(TreeNode root) {
dfs(root, new StringBuffer());
return res;
}
private void dfs(TreeNode root, StringBuffer cur) {
if(root == null) return;
cur.append(root.val);
if(root.left == null && root.right == null) {
res += Integer.parseInt(cur.toString());
}
dfs(root.left, cur);
dfs(root.right, cur);
cur.deleteCharAt(cur.length() - 1);
}
}
// 递归
func sumNumbers(root *TreeNode) (res int) {
var dfs func(root *TreeNode, sum int)
dfs = func(root *TreeNode, sum int) {
if root == nil {
return
}
if root.Left == nil && root.Right == nil {
res += (sum)*10 + root.Val
}
dfs(root.Left, sum*10+root.Val)
dfs(root.Right, sum*10+root.Val)
}
dfs(root, 0)
return
}
// 非递归
type pair struct {
sum int
node *TreeNode
}
func sumNumbers(root *TreeNode) (res int) {
if root == nil {
return 0
}
queue := make([]*pair, 0)
queue = append(queue, &pair{sum: root.Val, node: root})
for len(queue) != 0 {
pop := queue[0]
queue = queue[1:]
if pop.node.Left == nil && pop.node.Right == nil {
res += pop.sum
}
if pop.node.Left != nil {
queue = append(queue, &pair{
sum: pop.sum*10 + pop.node.Left.Val,
node: pop.node.Left,
})
}
if pop.node.Right != nil {
queue = append(queue, &pair{
sum: pop.sum*10 + pop.node.Right.Val,
node: pop.node.Right,
})
}
}
return
}
105. 从前序与中序遍历序列构造二叉树
给定两个整数数组 preorder 和 inorder ,其中 preorder 是二叉树的先序遍历, inorder 是同一棵树的中序遍历,请构造二叉树并返回其根节点。

解题思路
先序遍历用数组存的话,保存顺序是头 + 左子树 + 右子树;中序遍历保存顺序是:左子树 + 头 + 右子树;所以可以在preoder的第一位找到头是哪个,然后再找到头在中序遍历哪一位以确定左子树长度与右子树长度;然后分别递归去构造左右子树得到结果。具体操作如下:
首先定义一个辅助函数 dfs(preorder, pl, pr, inorder, il, ir),其中 preorder 和 inorder 分别表示前序遍历和中序遍历序列,pl、pr、il 和 ir 分别表示当前子树的前序遍历序列和中序遍历序列的边界。
- 如果 pl > pr 或 il > ir,表示当前子树为空,返回 nullptr。
- 在中序遍历序列中查找与当前前序遍历序列首元素相等的元素的下标 idx。该元素就是当前子树的根节点。
- 创建一个新的树节点 root,其值为前序遍历序列首元素(preorder[pl])。
- 计算左子树的节点数量 lenl(即中序遍历序列中根节点左边的元素数量,lenl = idx - il)。
- 递归构建左子树,递归调用 dfs(preorder, pl + 1, pl + lenl, inorder, il, idx - 1)。
- 递归构建右子树,递归调用 dfs(preorder, pl + lenl + 1, pr, inorder, idx + 1, ir)。
- 返回 root,表示已经构建完成当前子树。
在 buildTree 函数中,调用 dfs 函数开始递归构建二叉树,并返回构建完成的二叉树根节点。
/**
* Definition for a binary tree node.
* struct TreeNode {
* int val;
* TreeNode *left;
* TreeNode *right;
* TreeNode() : val(0), left(nullptr), right(nullptr) {}
* TreeNode(int x) : val(x), left(nullptr), right(nullptr) {}
* TreeNode(int x, TreeNode *left, TreeNode *right) : val(x), left(left), right(right) {}
* };
*/
class Solution {
public:
TreeNode* dfs(vector<int>& preorder, int pl, int pr, vector<int>& inorder, int il, int ir) {
if(pl > pr || il > ir) {
return nullptr;
}
int idx = il;
for(idx; idx <= ir; idx++) {
if(inorder[idx] == preorder[pl]) {
break;
}
}
TreeNode* root = new TreeNode(preorder[pl]);
int lenl = idx - il;
root->left = dfs(preorder,pl + 1, pl + lenl, inorder, il, idx - 1);
root->right = dfs(preorder, pl + lenl + 1, pr, inorder, idx + 1, ir);
return root;
}
TreeNode* buildTree(vector<int>& preorder, vector<int>& inorder) {
return dfs(preorder, 0, preorder.size() - 1, inorder, 0, inorder.size() - 1);
}
};
/**
* Definition for a binary tree node.
* public class TreeNode {
* int val;
* TreeNode left;
* TreeNode right;
* TreeNode(int x) { val = x; }
* }
*/
class Solution {
public TreeNode buildTree(int[] preorder, int[] inorder) {
return dfs(preorder, 0, preorder.length - 1, inorder, 0, inorder.length - 1);
}
private TreeNode dfs(int[] preorder, int pl, int pr, int[] inorder, int il, int ir) {
if (pl > pr || il > ir) {
return null;
}
int idx = il;
for (idx = il; idx <= ir; idx++) {
if (inorder[idx] == preorder[pl]) {
break;
}
}
TreeNode root = new TreeNode(preorder[pl]);
int lenl = idx - il;
root.left = dfs(preorder, pl + 1, pl + lenl, inorder, il, idx - 1);
root.right = dfs(preorder, pl + lenl + 1, pr, inorder, idx + 1, ir);
return root;
}
}
/**
* Definition for a binary tree node.
* type TreeNode struct {
* Val int
* Left *TreeNode
* Right *TreeNode
* }
*/
func buildTree(preorder []int, inorder []int) *TreeNode {
return dfs(preorder, 0, len(preorder)-1, inorder, 0, len(inorder)-1)
}
func dfs(preorder []int, pl int, pr int, inorder []int, il int, ir int) *TreeNode {
if pl > pr || il > ir {
return nil
}
var idx int
for idx = il; idx <= ir; idx++ {
if inorder[idx] == preorder[pl] {
break
}
}
root := &TreeNode{Val: preorder[pl]}
lenl := idx - il
root.Left = dfs(preorder, pl+1, pl+lenl, inorder, il, idx-1)
root.Right = dfs(preorder, pl+lenl+1, pr, inorder, idx+1, ir)
return root
}
297. 二叉树的序列化与反序列化
序列化是将一个数据结构或者对象转换为连续的比特位的操作,进而可以将转换后的数据存储在一个文件或者内存中,同时也可以通过网络传输到另一个计算机环境,采取相反方式重构得到原数据。
请设计一个算法来实现二叉树的序列化与反序列化。这里不限定你的序列 / 反序列化算法执行逻辑,你只需要保证一个二叉树可以被序列化为一个字符串并且将这个字符串反序列化为原始的树结构。
提示: 输入输出格式与 LeetCode 目前使用的方式一致,详情请参阅 LeetCode 序列化二叉树的格式。你并非必须采取这种方式,你也可以采用其他的方法解决这个问题。
解题思路
序列化可以用先序,中序,后序,层序;具体遍历方式可以是递归与迭代;下面用递归和迭代两种思路具体讲解:
解题思路一:递归(先序遍历)
- serialize:将二叉树序列化为字符串。
- 如果当前节点为空,返回字符 "#"。
- 对于非空节点,将节点的值以及左右子树的序列化结果拼接为一个字符串。
- deserializeProcess:用于反序列化的递归辅助函数。
- 从输入流中读取一个字符串。
- 如果字符串为 "#",表示空节点,返回空指针。
- 否则,创建一个新的 TreeNode,并将字符串转换为整数作为节点的值。
- 递归处理左右子树,并将结果分别作为当前节点的左右子节点。
- deserialize:将序列化的字符串转换回二叉树。
- 将输入的字符串转换为一个输入字符串流。
- 调用 deserializeProcess 函数递归构建二叉树,并返回根节点。
解题思路二:迭代(层序遍历)
- serialize:将二叉树序列化为字符串。
- 初始化一个队列,将根节点加入队列。
- 当队列不为空时,进行以下操作:
- 取出队列的第一个节点(当前处理节点)。
- 如果当前节点为空,将 "#" 添加到结果字符串中。
- 如果当前节点非空,将节点的值添加到结果字符串中,并将其左右子节点加入队列。
- 返回序列化结果字符串。
- deserialize:将序列化的字符串转换回二叉树。
- 如果输入字符串为空,返回空指针。
- 使用输入字符串创建一个istringstream对象。
- 读取根节点的值并创建根节点,将根节点加入队列。
- 当队列不为空时,进行以下操作:
- 取出队列的第一个节点(当前处理节点)。
- 读取左子节点的值,如果不是 "#",创建左子节点并将其加入队列。
- 读取右子节点的值,如果不是 "#",创建右子节点并将其加入队列。
- 返回反序列化后的二叉树的根节点。
/**
* Definition for a binary tree node.
* struct TreeNode {
* int val;
* TreeNode *left;
* TreeNode *right;
* TreeNode(int x) : val(x), left(NULL), right(NULL) {}
* };
*/
// 递归
class Codec {
public:
string serialize(TreeNode* root) {
if(root == nullptr) {
return "#";
}
return to_string(root->val) + ' ' + serialize(root->left) + ' ' + serialize(root->right);
}
TreeNode* deserializeProcess(istringstream& ss) {
string s;
ss >> s;
if(s == "#") {
return nullptr;
}
TreeNode* cur = new TreeNode(stoi(s));
cur->left = deserializeProcess(ss);
cur->right = deserializeProcess(ss);
return cur;
}
TreeNode* deserialize(string data) {
istringstream ss(data);
return deserializeProcess(ss);
}
};
// 迭代
class Codec {
public:
string serialize(TreeNode* root) {
if (root == nullptr) {
return "";
}
queue<TreeNode*> q;
q.push(root);
string result = "";
while (!q.empty()) {
TreeNode* cur = q.front();
q.pop();
if (cur == nullptr) {
result += "# ";
} else {
result += to_string(cur->val) + ' ';
q.push(cur->left);
q.push(cur->right);
}
}
return result;
}
TreeNode* deserialize(string data) {
if (data.empty()) {
return nullptr;
}
istringstream ss(data);
string val;
ss >> val;
TreeNode* root = new TreeNode(stoi(val));
queue<TreeNode*> q;
q.push(root);
while (!q.empty()) {
TreeNode* cur = q.front();
q.pop();
ss >> val;
if (val != "#") {
cur->left = new TreeNode(stoi(val));
q.push(cur->left);
}
ss >> val;
if (val != "#") {
cur->right = new TreeNode(stoi(val));
q.push(cur->right);
}
}
return root;
}
};
/**
* Definition for a binary tree node.
* public class TreeNode {
* int val;
* TreeNode left;
* TreeNode right;
* TreeNode(int x) { val = x; }
* }
*/
// 递归
public class Codec {
public String serialize(TreeNode root) {
if (root == null) {
return "#";
}
return Integer.toString(root.val) + ' ' + serialize(root.left) + ' ' + serialize(root.right);
}
private TreeNode deserializeProcess(Scanner scanner) {
if (!scanner.hasNext()) {
return null;
}
String s = scanner.next();
if (s.equals("#")) {
return null;
}
TreeNode cur = new TreeNode(Integer.parseInt(s));
cur.left = deserializeProcess(scanner);
cur.right = deserializeProcess(scanner);
return cur;
}
public TreeNode deserialize(String data) {
Scanner scanner = new Scanner(data);
return deserializeProcess(scanner);
}
}
// 迭代
import java.util.*;
public class Codec {
public String serialize(TreeNode root) {
if (root == null) {
return "";
}
Queue<TreeNode> q = new LinkedList<>();
q.offer(root);
StringBuilder result = new StringBuilder();
while (!q.isEmpty()) {
TreeNode cur = q.poll();
if (cur == null) {
result.append("# ");
} else {
result.append(cur.val).append(' ');
q.offer(cur.left);
q.offer(cur.right);
}
}
return result.toString();
}
public TreeNode deserialize(String data) {
if (data.isEmpty()) {
return null;
}
Scanner scanner = new Scanner(data);
String val = scanner.next();
TreeNode root = new TreeNode(Integer.parseInt(val));
Queue<TreeNode> q = new LinkedList<>();
q.offer(root);
while (!q.isEmpty()) {
TreeNode cur = q.poll();
if (scanner.hasNext()) {
val = scanner.next();
if (!val.equals("#")) {
cur.left = new TreeNode(Integer.parseInt(val));
q.offer(cur.left);
}
}
if (scanner.hasNext()) {
val = scanner.next();
if (!val.equals("#")) {
cur.right = new TreeNode(Integer.parseInt(val));
q.offer(cur.right);
}
}
}
return root;
}
}
// 递归
import (
"strconv"
"strings"
)
type Codec struct {
}
func Constructor() Codec {
return Codec{}
}
func (this *Codec) serialize(root *TreeNode) string {
if root == nil {
return "#"
}
return strconv.Itoa(root.Val) + " " + this.serialize(root.Left) + " " + this.serialize(root.Right)
}
func (this *Codec) deserializeProcess(ss []string, index *int) *TreeNode {
if *index >= len(ss) {
return nil
}
s := ss[*index]
*index = *index + 1
if s == "#" {
return nil
}
val, _ := strconv.Atoi(s)
cur := &TreeNode{Val: val}
cur.Left = this.deserializeProcess(ss, index)
cur.Right = this.deserializeProcess(ss, index)
return cur
}
func (this *Codec) deserialize(data string) *TreeNode {
ss := strings.Split(data, " ")
index := 0
return this.deserializeProcess(ss, &index)
}
// 迭代
import (
"strconv"
"strings"
)
type Codec struct {
}
func Constructor() Codec {
return Codec{}
}
func (this *Codec) serialize(root *TreeNode) string {
if root == nil {
return ""
}
var q []*TreeNode
q = append(q, root)
var result strings.Builder
for len(q) > 0 {
cur := q[0]
q = q[1:]
if cur == nil {
result.WriteString("# ")
} else {
result.WriteString(strconv.Itoa(cur.Val) + " ")
q = append(q, cur.Left)
q = append(q, cur.Right)
}
}
return result.String()
}
func (this *Codec) deserialize(data string) *TreeNode {
if data == "" {
return nil
}
ss := strings.Split(data, " ")
val := ss[0]
rootVal, _ := strconv.Atoi(val)
root := &TreeNode{Val: rootVal}
var q []*TreeNode
q = append(q, root)
index := 1
for len(q) > 0 {
cur := q[0]
q = q[1:]
if index < len(ss) {
val = ss[index]
index++
if val != "#" {
leftVal, _ := strconv.Atoi(val)
cur.Left = &TreeNode{Val: leftVal}
q = append(q, cur.Left)
}
}
if index < len(ss) {
val = ss[index]
index++
if val != "#" {
rightVal, _ := strconv.Atoi(val)
cur.Right = &TreeNode{Val: rightVal}
q = append(q, cur.Right)
}
}
}
return root
}
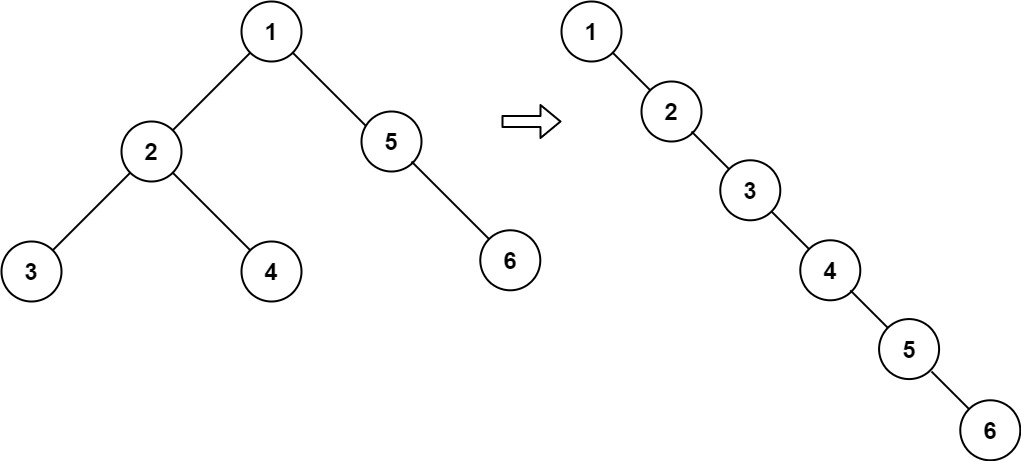
114. 二叉树展开为链表
给你二叉树的根结点 root ,请你将它展开为一个单链表:
展开后的单链表应该同样使用 TreeNode ,其中 right 子指针指向链表中下一个结点,而左子指针始终为 null 。
展开后的单链表应该与二叉树 先序遍历 顺序相同。
解题思路
这道题如果用递归注意一下保存left与right,递归的解题思路如下:
- 定义一个哨兵节点
org,其初始值为 -1,以及一个指针pre,初始指向org节点。 - 定义一个递归函数
flatten,输入参数为当前需要处理的节点root。 - 如果当前节点
root为空,直接返回,不做任何处理。 - 保存当前节点
root的左子树和右子树到临时变量left和right。 - 将指针
pre的左子节点设为nullptr,将其右子节点设为当前节点root。这样,pre节点总是指向最后一个已经展开的节点。 - 更新指针
pre,令其指向当前节点root。 - 递归调用
flatten函数,处理保存的左子树left。 - 递归调用
flatten函数,处理保存的右子树right。
这个过程会递归地展开整棵树,并将展开后的节点串起来形成一个单链表。最后,在调用 flatten 函数时,传入根节点即可完成整棵树的展开。
/**
* Definition for a binary tree node.
* struct TreeNode {
* int val;
* TreeNode *left;
* TreeNode *right;
* TreeNode() : val(0), left(nullptr), right(nullptr) {}
* TreeNode(int x) : val(x), left(nullptr), right(nullptr) {}
* TreeNode(int x, TreeNode *left, TreeNode *right) : val(x), left(left), right(right) {}
* };
*/
class Solution {
public:
TreeNode* org = new TreeNode(-1);
TreeNode* pre = org;
void flatten(TreeNode* root) {
if(root == nullptr) {
return;
}
TreeNode* left = root->left;
TreeNode* right = root->right;
pre->left = nullptr;
pre->right = root;
pre = root;
flatten(left);
flatten(right);
}
};
public class Solution {
private TreeNode org = new TreeNode(-1);
private TreeNode pre = org;
public void flatten(TreeNode root) {
if (root == null) {
return;
}
TreeNode left = root.left;
TreeNode right = root.right;
pre.left = null;
pre.right = root;
pre = root;
flatten(left);
flatten(right);
}
}
func flatten(root *TreeNode) {
var pre *TreeNode = &TreeNode{Val: -1}
var flattenHelper func(node *TreeNode)
flattenHelper = func(node *TreeNode) {
if node == nil {
return
}
left := node.Left
right := node.Right
pre.Left = nil
pre.Right = node
pre = node
flattenHelper(left)
flattenHelper(right)
}
flattenHelper(root)
}
剑指 Offer 36. 二叉搜索树与双向链表
输入一棵二叉搜索树,将该二叉搜索树转换成一个排序的循环双向链表。要求不能创建任何新的节点,只能调整树中节点指针的指向。
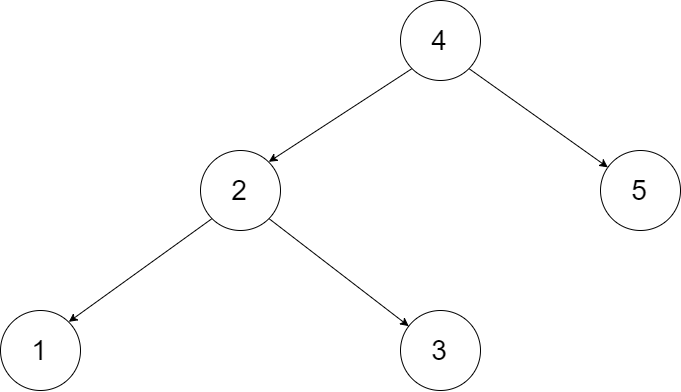
为了让您更好地理解问题,以下面的二叉搜索树为例:
我们希望将这个二叉搜索树转化为双向循环链表。链表中的每个节点都有一个前驱和后继指针。对于双向循环链表,第一个节点的前驱是最后一个节点,最后一个节点的后继是第一个节点。
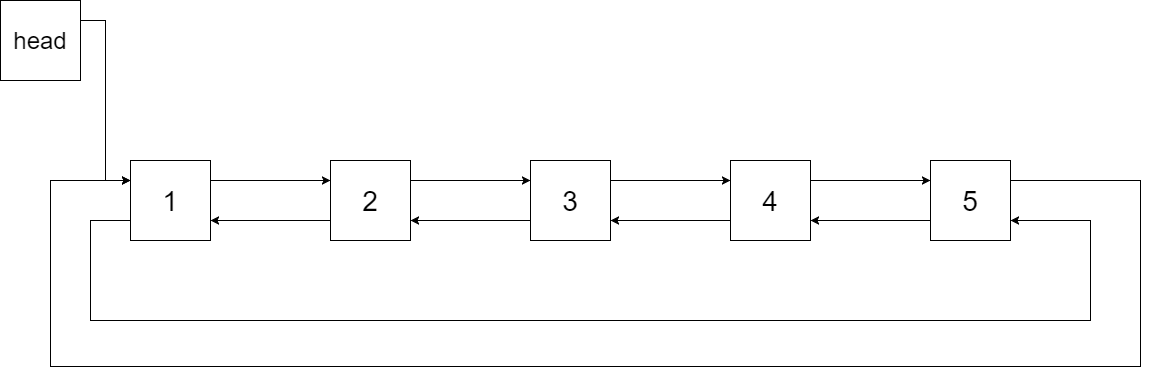
下图展示了上面的二叉搜索树转化成的链表。“head” 表示指向链表中有最小元素的节点。
特别地,我们希望可以就地完成转换操作。当转化完成以后,树中节点的左指针需要指向前驱,树中节点的右指针需要指向后继。还需要返回链表中的第一个节点的指针。
解题思路
BST的中序遍历就可以用于排序,具体操作如下:
在类 Solution 中定义了三个成员变量:
- org:一个新的链表节点,用作哨兵节点,其初始值为 -1。
- pre:一个指向链表节点的指针,用于记录上一个遍历到的节点。
- flag:一个整数,用于判断是否是第一个遍历到的节点。
函数 dfs() 负责具体的中序遍历:
- 如果 root 为空,直接返回。
- 对 root 的左子树进行中序遍历:dfs(root->left)。
- 判断是否是第一个节点,如果是,则将 org 节点的右子树指向 root,将 pre 指针指向 root,同时将 flag 设置为 1。否则,将 pre 节点的右子树指向 root,并更新 pre 指针为当前 root。
- 对 root 的右子树进行中序遍历:dfs(root->right)。
函数 treeToDoublyList() 负责返回中序遍历的结果:
- 创建一个新的哨兵节点 org,并将 pre 指针指向 org。
- 调用 dfs(root) 函数,对二叉搜索树进行中序遍历。
- 初始化 cur 指针指向 org 节点的右子树,pre 指针指向 org。
- 遍历 cur 指针,为每个节点设置 left 指针。
- 记录第一个节点(first)和最后一个节点(back)。
- 如果第一个节点 first 不为空,则将 first 的 left 指针指向 back,将 back 的 right 指针指向 first,以完成循环双向链表的连接。
- 返回 org 节点的右子树。
/*
// Definition for a Node.
class Node {
public:
int val;
Node* left;
Node* right;
Node() {}
Node(int _val) {
val = _val;
left = NULL;
right = NULL;
}
Node(int _val, Node* _left, Node* _right) {
val = _val;
left = _left;
right = _right;
}
};
*/
class Solution {
public:
Node* pre = nullptr;
Node* head = nullptr;
void dfs(Node* root) {
if (root == nullptr) return;
dfs(root->left);
if (pre == nullptr) {
head = root;
} else {
pre->right = root;
root->left = pre;
}
pre = root;
dfs(root->right);
}
Node* treeToDoublyList(Node* root) {
if (root == nullptr) return nullptr;
dfs(root);
head->left = pre;
pre->right = head;
return head;
}
};
public class Solution {
private Node pre = null;
private Node head = null;
private void dfs(Node root) {
if (root == null) {
return;
}
dfs(root.left);
if (pre == null) {
head = root;
} else {
pre.right = root;
root.left = pre;
}
pre = root;
dfs(root.right);
}
public Node treeToDoublyList(Node root) {
if (root == null) {
return null;
}
dfs(root);
head.left = pre;
pre.right = head;
return head;
}
}
func treeToDoublyList(root *Node) *Node {
var pre, head *Node
var dfs func(node *Node)
dfs = func(node *Node) {
if node == nil {
return
}
dfs(node.Left)
if pre == nil {
head = node
} else {
pre.Right = node
node.Left = pre
}
pre = node
dfs(node.Right)
}
if root == nil {
return nil
}
dfs(root)
head.Left = pre
pre.Right = head
return head
}